Preserving soil fertility
Good farm management begins with rigorous crop planning. Crop rotation alternates different plants on the same plot to maintain soil fertility, reduce disease risks, and limit pesticide use. This strategy also optimizes long-term yields and promotes an ecological balance that benefits soil health.

Ensuring the profitability of a farm requires precise financial monitoring. This involves controlling expenses and evaluating necessary investments.

Respect natural cycles
Work with nature’s rhythms to promote soil
and plant health.

Use organic fertilizers
Use compost, manure, and natural amendments to enrich the soil without chemicals.

Preserving biodiversity
Encourage crop and species diversity to strengthen agricultural ecosystems.

Biological pest control
Promote natural predators and non-chemical methods to protect crops.
Crop rotation and intercropping
Alternate and combine plants to prevent disease and improve soil fertility.
Sustainable water management
Optimize irrigation and preserve water resources by avoiding waste.
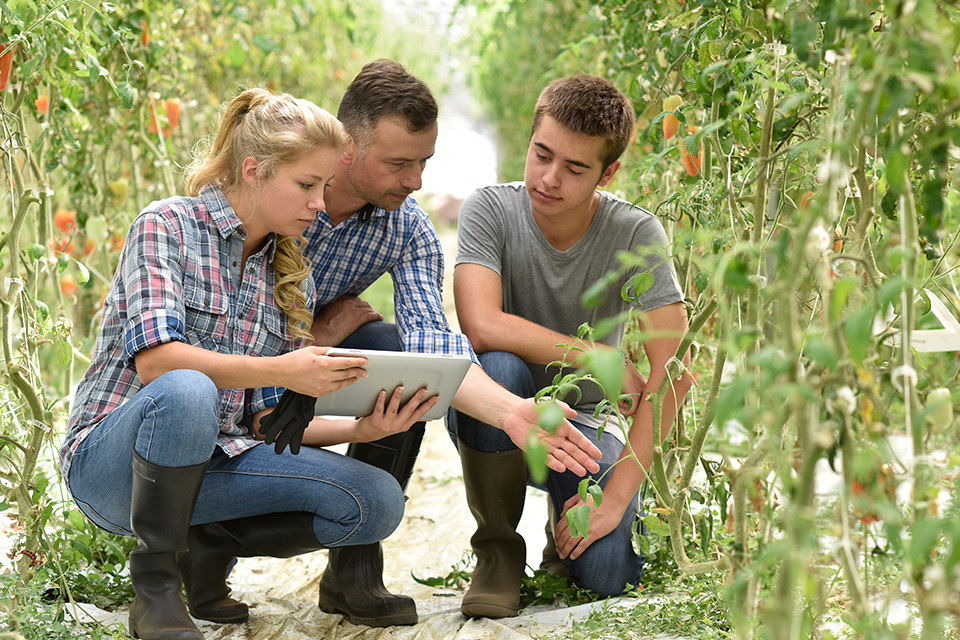

Training for modern agriculture
Training plays a key role in the evolution of modern agriculture by enabling professionals to acquire the necessary technical, technological, and managerial skills. It facilitates the adoption of innovations such as precision agriculture, connected machinery, and sustainable practices. This includes mastering the use of essential equipment like the straw blower, the silage block cutter, and the feeding bucket, which contribute to more efficient livestock management. By strengthening know-how and raising awareness of environmental issues, training helps make farms more efficient, resilient, and environmentally friendly. Furthermore, it paves the way for new careers and encourages career change, thus addressing current and future challenges in the agricultural sector.

Farmer
Cultivate, raise livestock, and manage the farm on a daily basis

Agricultural technician
Optimize practices and master agricultural tools

Agronomic engineer
Innovate for sustainable and efficient agriculture
Key Challenges of the Modern Agri-Food Industry
The agri-food industry plays a central role in transforming agricultural raw materials into food products for consumers. It must address several major challenges, including ensuring food safety through rigorous controls, while innovating to meet growing expectations for health and sustainability. Furthermore, environmental impact management is becoming essential, with efforts to reduce waste, limit resource use, and adopt eco-friendly packaging.
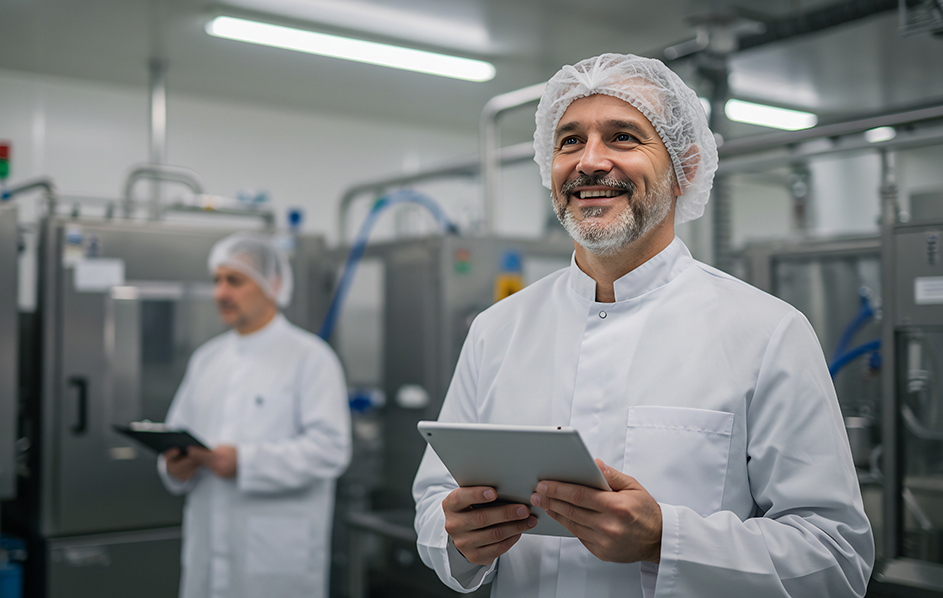

Agricultural innovation
Automation in Modern Agriculture
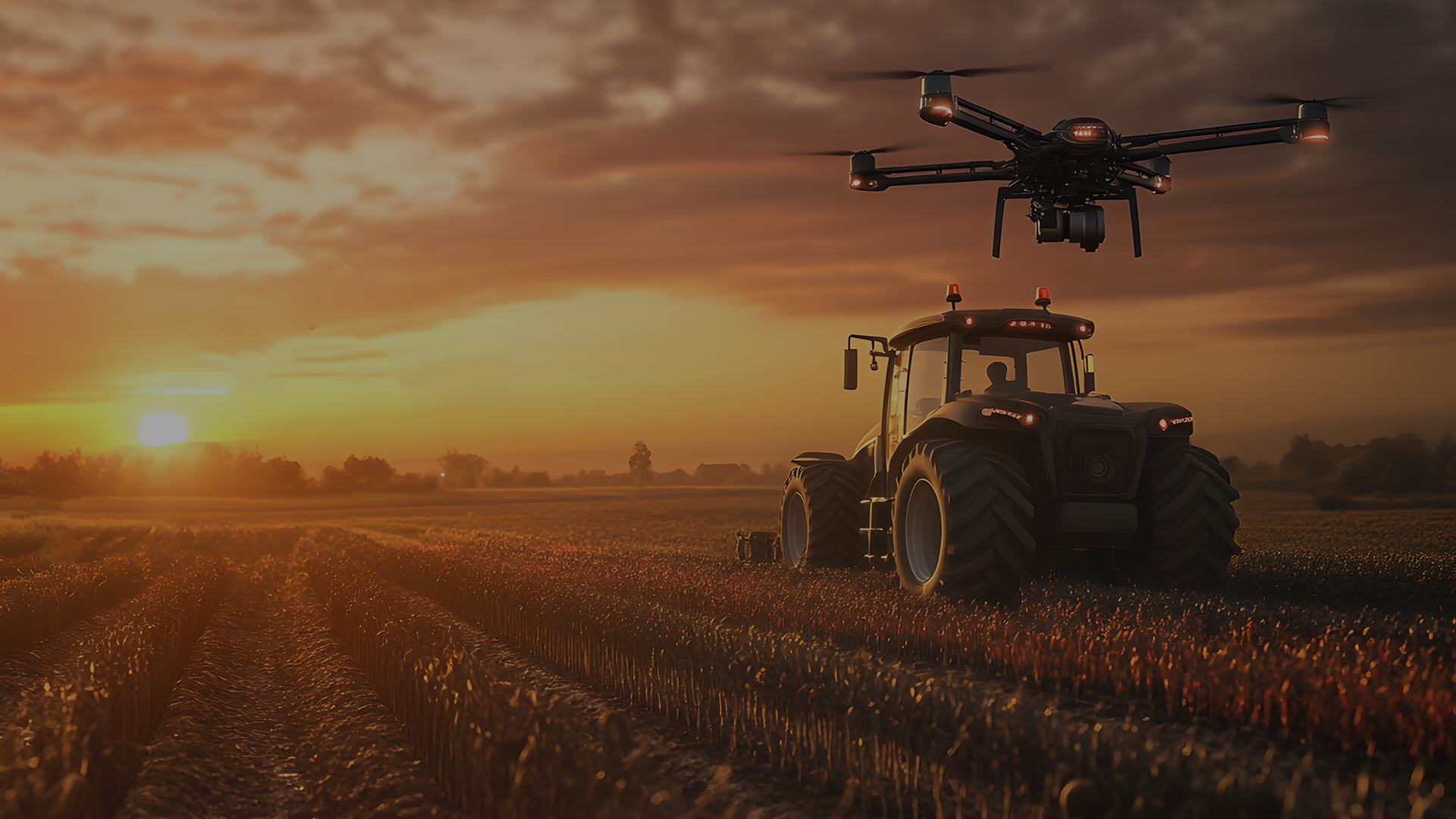
The integration of automation into agriculture is profoundly transforming farming practices by making operations more precise and efficient. Through the use of robots, drones, and smart sensors, farmers can monitor crop health in real time, optimize the use of resources such as water and fertilizers, and reduce the arduousness of repetitive tasks.
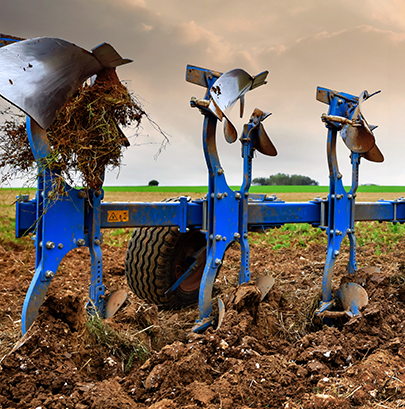

The plow
A traditional tool used to turn over and loosen the soil before sowing.
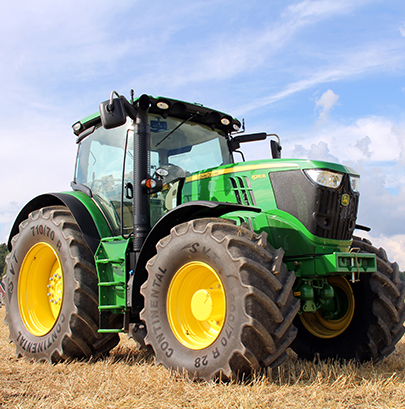

The tractor
Versatile machine that facilitates soil cultivation and transport.
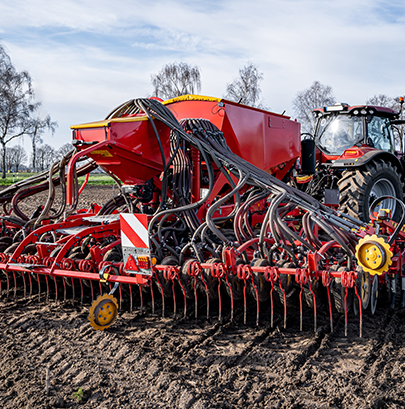

The seeder
A mechanical tool used to sow seeds precisely and evenly across fields.

